Lead by Dr Guy Woodward (Imperial)
Co-Leaders: Dr Sian Griffiths (Cardiff)
Dr David Noble (BTO)
Dr Rachel Chalmers (PHW)
Dr Isabelle Durance (Cardiff)
Laura Evans (Cardiff)
Dr Hugh Feeley (Cardiff)
Dr Jonathan Grey (QMUL)
Dr Kat Layer (Imperial)
Prof Steve Ormerod (Cardiff)
Dr Dan Perkins (Imperial)
Marian Pye (Cardiff)
Dr Guy Robinson (PHW)
Dr Isa-Rira Russo (Cardiff)
Prof Andrew Weightman (Cardiff)

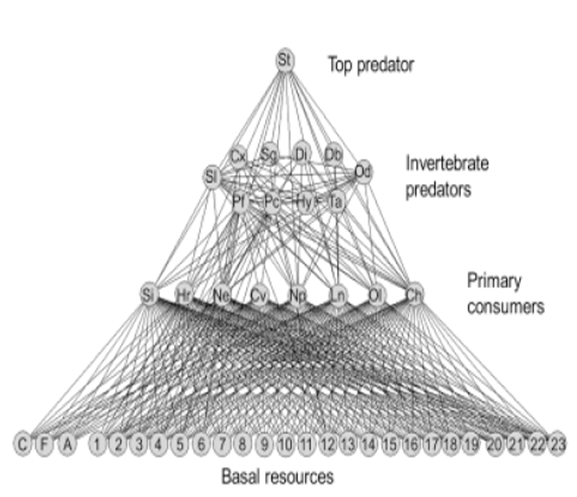
The food web approach: Layer et al. 2011 GCB
There are three key questions to be investigated in theme two:
- What aspects of diversity in food webs are linked to services?
- How can these be quantified most effectively?
- What measures are most appropriate to monitor biologically mediated ecosystem services?

This theme will provide us with the experimental data to feed back into the project and is split into three components:
a) Fish and Bird Ecosystem ServicesHere we ask what are the Ecosystem Service relevant meanings of biodiversity such as:
- fish abundance and type
- fish size and growth
- bird abundance and type
- invertebrate abundance and type as prey of suitable quality
- whole food web structure and dynamics in producing prey in sufficient quantity.
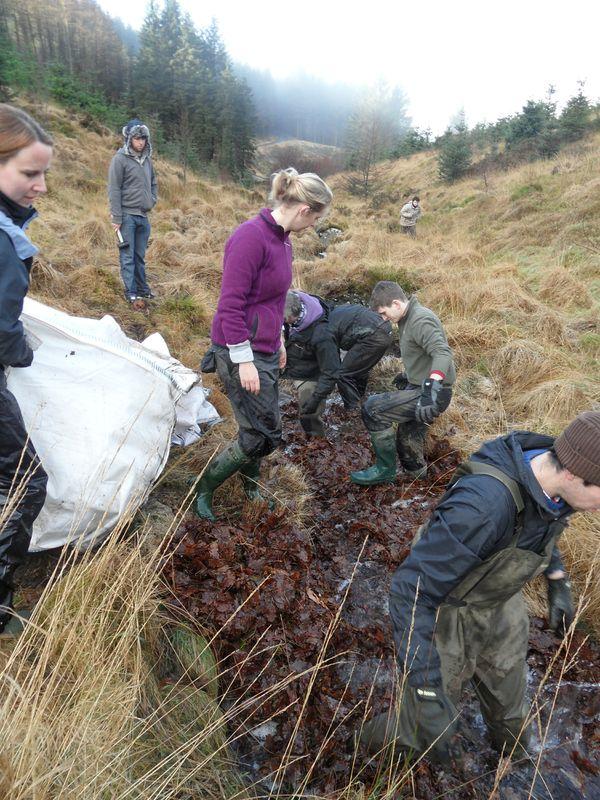

Leaf litter addition – January 2013
b) Water Quality and Decomposition, Experimental Work
Three factorial experiments will be carried out to assess the role of river biota in regulating water quality and decomposition:
- Leaf litter addition
A test of land use change to broadleaf trees – Winter 2012/2013 - N addition
A test of land use change to pasture – Spring 2014 - C addition
A test of land use and climate changes – Spring 2014
c) Regulation of water quality: the case of pathogens
Pioneering research seeks to assess the role of river biota in regulating or facilitating pathogen flow. Cryptosporidium is of particular interest to water companies as they cannot be removed from drinking water through traditional water treatments. We will:
- Assess the distribution of Cryptosporidium in wild and domestic hosts and vectors in upland catchments.
- Investigate the genetic diversity of isolates using high resolution genotyping.

The decomposition experiment is now complete and full details of the twelve tons of leaf litter, 288 biofilm bricks and 576 litter bags to measure microbes and invertebrates are given in our video:
In summer 2012 sampling was carried out to look at food web structure from biofilm to fish across upland Wales. Over 800 fish were identified, weighed, and sized and more than 18000 samples of diatoms identified and sized.
Bird sampling is currently being carried out (summer 2013) by the BTO team.
The Public Health Wales, Imperial and Cardiff teams are underway with their work to assess the distribution and species of Cryptosporidium present in our rivers.



